Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 ray dose rate in nuclear fusion reactor
ray dose rate in nuclear fusion reactorSato, Satoshi; Kawasaki, Nobuo*; Kume, Etsuo; Nishitani, Takeo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.62 - 65, 2004/03
no abstracts in English
Sato, Satoshi; Morioka, Atsuhiko; Kinno, Masaharu*; Ochiai, Kentaro; Hori, Junichi; Nishitani, Takeo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.66 - 69, 2004/03
no abstracts in English
Tsuda, Shuichi; Endo, Akira; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.132 - 135, 2004/03
A solid material improved in hydrogen and oxygen contents was synthesized for development of a physical phantom for neutron. The elemental composition and density are aimed for those of the soft tissue in ICRU Report 44. The soft tissue equivalence has been verified by an absorbed dose measurement using a 252Cf neutron source. In the present work, absorbed doses were measured for the purpose of examinations of the characteristic of the synthesized soft tissue substitute for neutron of various energies, using mono-energetic 0.565 MeV neutrons from  Li(p,n) reaction and 5 MeV from D(d,n) reaction, and quasi-mono-energetic ones (40 and 65 MeV) produced via
Li(p,n) reaction and 5 MeV from D(d,n) reaction, and quasi-mono-energetic ones (40 and 65 MeV) produced via  Li(p,n) reaction. The measured absorbed doses were compared with those calculated by Monte Carlo simulation codes. The results indicate that the tissue substitute has a characteristic of soft tissue equivalence for neutron in the energy range from several hundred keV up to approximately 100 MeV.
Li(p,n) reaction. The measured absorbed doses were compared with those calculated by Monte Carlo simulation codes. The results indicate that the tissue substitute has a characteristic of soft tissue equivalence for neutron in the energy range from several hundred keV up to approximately 100 MeV.
Morimoto, Yuichi*; Ochiai, Kentaro; Nishio, Takashi*; Wada, Masayuki*; Yamauchi, Michinori*; Nishitani, Takeo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.42 - 45, 2004/03
no abstracts in English
Kai, Tetsuya; Harada, Masahide; Maekawa, Fujio; Teshigawara, Makoto; Konno, Chikara; Ikeda, Yujiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.172 - 175, 2004/03
In J-PARC neutron source, intense protons (3 GeV,1 MW) pass through a proton-beam window and bombard a Hg target in a target-moderator-reflector-assembly (TMRA). The SS316 target chamber is the most highly activated. Decouplers (Ag-In-Cd (AIC) alloy) are also highly activated. Some neutron extraction holes of Be and AL-coated iron reflector are lined with AIC alloy. A SS316 shield is located outer the TMRA. All these components are cooled by H O or D
O or D O. We estimated the induced-radioactivity of the TMRA components and the cooling water using NMTC/JAM, MCNP4 and DCHAIN-SP. As results, the remote maintenance and massive shields were indispensable. For example, a 30 cm thick Fe cask for the reflector assembly was necessary to attenuate the radiation less than 1 mSv/h. The cask required a 130-ton crane. The AL-coated Fe of the reflector was adopted instead of SS316 resulting in eliminating the high activity of Ni in SS316 and reduction of the cask weight. Based on these results, shielding wall designs and maintenance scenarios of the highly activated components are developed.
O. We estimated the induced-radioactivity of the TMRA components and the cooling water using NMTC/JAM, MCNP4 and DCHAIN-SP. As results, the remote maintenance and massive shields were indispensable. For example, a 30 cm thick Fe cask for the reflector assembly was necessary to attenuate the radiation less than 1 mSv/h. The cask required a 130-ton crane. The AL-coated Fe of the reflector was adopted instead of SS316 resulting in eliminating the high activity of Ni in SS316 and reduction of the cask weight. Based on these results, shielding wall designs and maintenance scenarios of the highly activated components are developed.
Kinase, Sakae; Zankl, M.*; Funabiki, Jun*; Noguchi, Hiroshi; Saito, Kimiaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.136 - 139, 2004/03
The present study was performed to evaluate S values to the urinary bladder wall for several beta-ray emitters such as  C,
C,  Na,
Na,  P,
P,  Co,
Co, 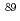 Sr,
Sr,  Sr,
Sr,  Y,
Y, 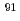 Y,
Y,  Cs,
Cs, 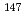 Pm and
Pm and  Tl for a MIRD 5 type phantom using Monte Carlo simulation. S values were also evaluated on the adult voxel phantoms developed at JAERI and were compared with those for the MIRD 5 type phantom. Furthermore, each of the S values was compared with those derived from the simple assumption (ICRP 30). Consequently, it was found that the absorbed dose to the urinary bladder wall for those radionuclides are not one-half of the absorbed dose in bladder content and largely depend on the mass of the urinary bladder wall. S values derived from the simple assumption were found to be conservative for beta-ray emitters within the urinary bladder.
Tl for a MIRD 5 type phantom using Monte Carlo simulation. S values were also evaluated on the adult voxel phantoms developed at JAERI and were compared with those for the MIRD 5 type phantom. Furthermore, each of the S values was compared with those derived from the simple assumption (ICRP 30). Consequently, it was found that the absorbed dose to the urinary bladder wall for those radionuclides are not one-half of the absorbed dose in bladder content and largely depend on the mass of the urinary bladder wall. S values derived from the simple assumption were found to be conservative for beta-ray emitters within the urinary bladder.
Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Hirayama, Hideo*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.498 - 501, 2004/03
JAERI-Universities Joint Research Project has been carried out to study the radiation safety in high-energy proton accelerator facilities since 2000. Ten groups from 2 research institutes and 5 universities joined in the project to tackle 3 major subjects below, using a quasi-monoenergetic neutron field at TIARA facility of JAERI. The groups had annual meetings to discuss the plan and progress of the studies and exchange their views for effective cooperation. (1)Studies on basic physical data necessary for neutron dosimetry. (2)Development of neutron monitors and dosimeters for several tens MeV region. (3)Studies on formation of radioactive aerosols and gases for internal dosimetry.
Morioka, Atsuhiko; Sato, Satoshi; Ochiai, Kentaro; Sakasai, Akira; Hori, Junichi; Yamauchi, Michinori*; Nishitani, Takeo; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Masaki, Kei; Sakurai, Shinji; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.109 - 112, 2004/03
Neutron shielding material of the port section of JT-60 superconducting modification (JT-60SC) serves as a design which used resin (KRAFTON-HB4) excellent in the temperature characteristic from polyethylene. In order to make port weight mitigate and reduce the nuclear heating of the superconducting coil, we were developed the resin which added natural BORON to resin. The 2.45MeV neutron generated in the D-D reaction was irradiated, the penetration of the neutron was measured in some kinds of samples which changed the amount of BORON, and the shielding performance of the resin containing BORON was compared with them. The penetration rates of fast neutron flux do not depend on the doped density of boron in both measurements. Whereas the penetration rates of thermal neutron flux in the resin with 2 wt% B are about 25% lower than those with 1 wt% at the back surface of the test specimens.
Sasa, Toshinobu; Oigawa, Hiroyuki; Tayama, Ryuichi*; Hayashi, Katsumi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.30 - 33, 2004/03
The construction of Transmutation Experimental Facility (TEF) is planned under the framework of Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) project. A liquid lead-bismuth (Pb-Bi) spallation target with beam power of 600MeV-200kW will be installed into the TEF. Analyses were performed to determine the effective thickness of biological shield for Pb-Bi target by using both MCNPX and ATRAS code system. Thickness of around 6m should be required to decrease the radiation level. The streaming analyses through the proton injection beam duct and the primary cooling circuit piping were also performed. The result of the beam duct streaming shows good agreement between the results of MCNPX and DUCT-III. The additional shield must be installed to suppress the activation of accelerator components. In the case of streaming through the primary cooling circuit piping, it is proved that the radiation level at the exit of the shield is allowable. The radiation level can be much more reduced by optimizing the bending position and length of the piping.
Matsuda, Norihiro; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Sasamoto, Nobuo*; Kinno, Masaharu*; Kitami, Takayuki; Ichimura, Takahito; Hori, Junichi*; Ochiai, Kentaro; Nishitani, Takeo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.74 - 77, 2004/03
In high power proton accelerator facilities, concrete shield can be highly activated, which makes maintenance work quite difficult. So, a low-activationized concrete (limestone concrete) is to be partially adopted as a concrete shield for Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) aiming at reducing  -ray exposure dose during maintenance period. A new quantity,
-ray exposure dose during maintenance period. A new quantity,  Na-equivalent, was introduced as a criterion to assure effectiveness of the low-activationized concrete. In order of its verification, powdered low-activationized concrete and ordinary one were irradiated using FNS at JAERI. The measurements were analyzed by a shielding design code system being used for J-PARC, showing that the calculations reproduce the measured induced activity within a factor of 2. Furthermore, by using the same code system,
Na-equivalent, was introduced as a criterion to assure effectiveness of the low-activationized concrete. In order of its verification, powdered low-activationized concrete and ordinary one were irradiated using FNS at JAERI. The measurements were analyzed by a shielding design code system being used for J-PARC, showing that the calculations reproduce the measured induced activity within a factor of 2. Furthermore, by using the same code system,  -ray exposure dose was calculated for the configuration of J-PARC to find out that
-ray exposure dose was calculated for the configuration of J-PARC to find out that  -ray exposure dose by the low-activationized concrete was about 10 times lower than that by the ordinary concrete in a period of less than a few days after operation.
-ray exposure dose by the low-activationized concrete was about 10 times lower than that by the ordinary concrete in a period of less than a few days after operation.
Masukawa, Fumihiro; Nakano, Hideo*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Sasamoto, Nobuo; Tayama, Ryuichi*; Hayashi, Katsumi*; Shin, Kazuo*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.46 - 49, 2004/03
A simple design code for duct-streaming radiations, DUCT-III was applied to the analyses of the streamed neutron spectra measured at TIARA labyrinth with two bends. The code satisfactorily reproduced the measured neutron energy spectra and the Monte Carlo calculations, except that every calculation overestimated the measured thermal components by factor of 2 or 3.
Kurihara, Osamu; Takasaki, Koji; Momose, Takumaro; Terakado, Yoshinori*; Takahashi, Koji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.243 - 246, 2004/03
None
Shimizu, Yoshio; Oka, Tsutomu
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.105 - 108, 2004/03
None
Tsujimura, Norio; Kanai, K.; Momose, Takumaro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.203 - 206, 2004/03
None
Endo, Akira; Kim, E.; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Yoshizawa, Michio; Tanaka, Susumu; Nakamura, Takashi; Rasolonjatovo, A. H. D.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.510 - 513, 2004/03
no abstracts in English
Nishitani, Takeo; Ochiai, Kentaro; Yoshida, Shigeo*; Tanaka, Ryohei*; Wakisaka, Masashi*; Nakao, Makoto*; Sato, Satoshi; Yamauchi, Michinori*; Hori, Junichi; Wada, Masayuki*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.58 - 61, 2004/03
no abstracts in English
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Tsuda, Shuichi; Sakamoto, Yukio; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Niita, Koji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.287 - 290, 2004/03
Radiological protection against heavy ions has been an essential issue in the planning of long term space missions. We performed Monte Carlo calculations of dose distributions in terms of the linear energy transfer (LET) of ionizing particles using Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, for incidences of various kinds of heavy ions with energies up to 3 GeV/A. Based on the results, we found that large amounts of energies are imparted by particles with an LET above 10 keV/mm even for the incidences of heavy ions with high energies. This tendency is different from that for high energy hadron incidences, where more than 80% of the total deposited energies are imparted by particles with an LET below 10 keV/mm.
Oguri, Tomomi*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Tanaka, Susumu; JAERI-University Collaboration Group for Accelerator Shielding Study
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.54 - 57, 2004/03
In shielding design of proton accelerator facilities, it applies simplified formulae and Monte Carlo calculation methods to calculation radiation streaming of access way and duct. A radiation streaming experiment was carried out in order to validate accuracy of intermediate energy region in labyrinth of access way connected to the 1st heavy ion room in TIARA at JAERI. In this paper, it is described comparing of measured data and calculations by MCNP-4B Monte Carlo code and simplified formulae. In Monte Carlo calculations, HILO86 constant set and LA150 was used for cross section data. The results of this experimental analysis show the accuracy of 50% errors for Monte Carlo calculations overall and a factor of 3 for simplified formulae. So applicability for these calculation methods in region of intermediate energy is validated.
Nakane, Yoshihiro; Sakamoto, Yukio; Tsuda, Shuichi; Tanaka, Susumu; Hirayama, Hideo*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.506 - 509, 2004/03
no abstracts in English
Nakano, Hideo*; Masukawa, Fumihiro; Nakashima, Hiroshi; Sasamoto, Nobuo*; Tayama, Ryuichi*; Handa, Hiroyuki*; Hayashi, Katsumi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.50 - 53, 2004/03
In order to estimate accuracy of the various calculation methods for the neutron streaming through a maze and duct in proton accelerator facilities, we performed benchmark analyses by using the radiation shielding design codes. According to the results of the benchmark analyses, it is concluded that NMTC/MCNP, MCNPX and DUCT-III are applicable to actual calculation of the duct-streaming radiations for J-PARC.
Verzilov, Y. M.; Ochiai, Kentaro; Nishitani, Takeo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.395 - 398, 2004/03
no abstracts in English